What Is Hyaline Cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage is a type of connective tissue found in various parts of the human body, characterized by its glossy and smooth appearance. Here are some key points about hyaline cartilage:
- Hyaline cartilage is the most common type of cartilage in the body.
- It has a glass-like (hyaline) and translucent appearance.
- It is found in areas such as the bones of free-moving joints (articular cartilage), the walls of the respiratory tract (e.g., bronchi, trachea), ribs, nose, and larynx.
- The color of hyaline cartilage is pearl-gray, and it has a firm consistency.
- It contains a significant amount of collagen, which provides structural support and strength.
- Hyaline cartilage is avascular, meaning it lacks blood vessels, and it is not innervated, meaning it has no nerves.
- It is relatively simple in structure compared to other types of cartilage.
- Hyaline cartilage plays a crucial role in providing smooth joint surfaces, supporting the respiratory system, and maintaining the shape and structure of certain body parts.
- While hyaline cartilage has some regenerative capacity, its ability to repair itself is limited compared to other tissues.
- Damage or deterioration of hyaline cartilage can lead to conditions like osteoarthritis, where the cartilage wears away, causing joint pain and dysfunction.
Overall, hyaline cartilage serves as an important connective tissue in the body, contributing to the proper functioning and structure of various organs and joints.
How Hyaline Cartilage Protects Your Joints
- Shock Absorption – Reduces the impact from walking, running, and jumping
- Friction Reduction – Creates a smooth surface so bones glide easily
- Weight Distribution – Spreads pressure evenly across the joint
- Joint Stability – Helps maintain bone alignment for safe movement
Role in Supporting Movement
The function of hyaline cartilage is crucial for the proper functioning and protection of various parts of the body. Here’s an overview of its functions based on the provided content:
- Support and Flexibility: Hyaline cartilage provides structural support and flexibility to different body structures. It can be found in the nose, ears, and the attachment points of the ribs to the sternum. It gives these body parts their form while allowing some flexibility.
- Articular Surface Protection: When hyaline cartilage is present on the articular surfaces of bones, it is called articular cartilage. Its primary function is to act as a shock absorber and reduce friction between bones at joints. Articular cartilage provides a smooth surface for movement and helps withstand the pressure and friction associated with weight-bearing activities.
- Support in the Respiratory System: In the respiratory system, hyaline cartilage provides support to softer tissues, such as the trachea and larynx. It helps maintain an open position in these structures, allowing for the passage of air.
- Mechanical Support in Development and Growth: Hyaline cartilage plays a vital role in the development and growth of bones. It provides mechanical support to developing bones and contributes to their proper formation.
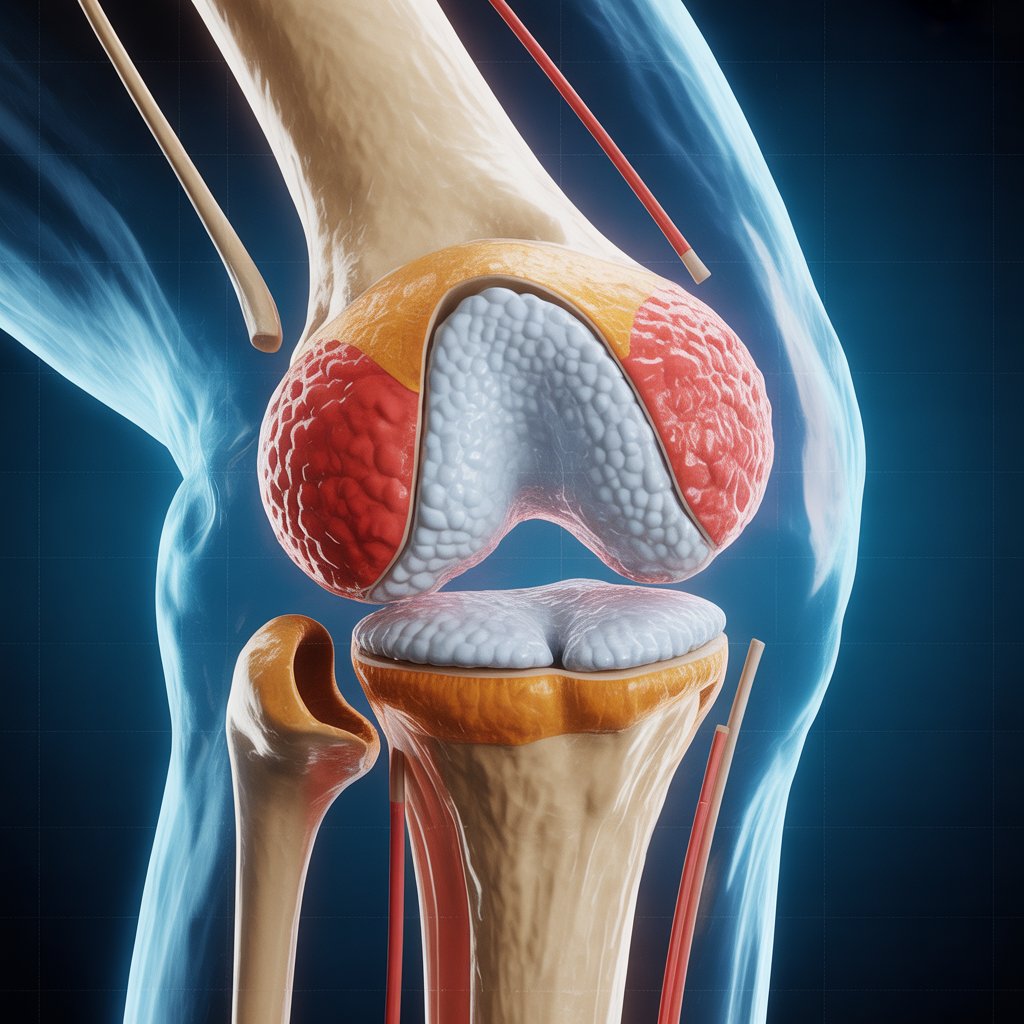
What Happens When Hyaline Cartilage Gets Damaged?
Damage to hyaline cartilage can be caused by:
- Injury – sudden impact or sports accidents
- Overuse – repetitive joint strain
- Aging – natural wear over time
This may lead to conditions like:
- Osteoarthritis – cartilage breakdown causing pain and stiffness
- Chondromalacia – softening and weakening of cartilage
How to Keep Hyaline Cartilage Healthy
Low-impact exercises can help to strengthen the muscles around the joints, preventing injuries and taking pressure off the joint itself. They can also help you maintain a healthy weight, which is important for reducing pressure on the joints and preventing further cartilage degeneration.
Treatment and Repair Options
Non-surgical treatments:
- Physiotherapy to strengthen surrounding muscles
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Joint injections (hyaluronic acid, PRP)
Surgical treatments:
- Microfracture surgery to stimulate cartilage growth
- Cartilage transplantation
- Stem cell therapy (emerging research)
Conclusion
Hyaline cartilage is your body’s natural shock absorber and movement facilitator. By protecting it through healthy habits, you can keep your joints functioning smoothly for years to come. Early diagnosis and care are key to avoiding long-term joint problems, so listen to your body and take action when needed.




Pingback: Why Pamban Bridge India is a Must-Visit Landmark in Tamil Nadu